Currently, the dominant battery technology is based on lithium. Simultaneously, the most promising outsider in the medium term seems to be solid batteries. However, other solutions could find a place in the world of electrification.
One such innovative solution is a supercapacitor. And if you are planning to buy it for use in electronics, you need to be mindful of a few factors to get your hands on the best one, like Murata supercapacitors.
What Are Supercapacitors?
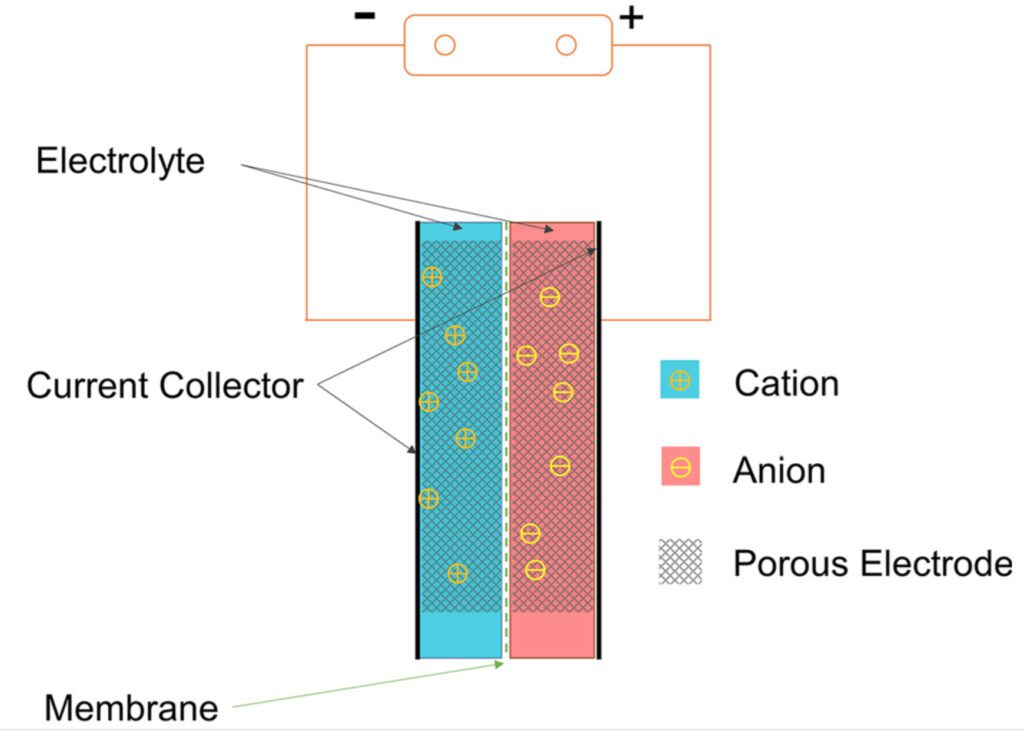
Supercapacitors are a cross between capacitors used in electronics and batteries. Like the latter, they have two electrodes, positive and negative, and an electrolyte. But, they accumulate energy in an electrostatic field and not through a chemical process. It allows them to instantly absorb and transmit higher powers with much faster charge and discharge cycles.
Factors to Consider
Here are a few features that a perfect supercapacitor must hold. Giving importance to these factors may help you in grabbing the best deal.
Charge Time
The charging and discharge periods of supercapacitors are approximately equal to those of ordinary capacitors. A strong charge and discharge current are feasible because of their low internal resistance. Batteries typically require a couple of hours to achieve a maximum charge level, for example, a mobile phone battery. Supercapacitors will hit the same charge state in two minutes or less.
Power
A specific power (also called specific energy) is a metric used to equate various technologies and choose the most efficient, for instance, the Murata supercapacitors. A supercapacitor may provide an individual capacity five to ten times greater than that of a cell. One battery type has a specific power of 1 – 3 kW/kg, whereas the specific power is 10 kW/kg. This property is vital in every application that calls for periodic energy releases from the storage system.
Cycle Life and Safety
When mistreated, supercapacitors are better than regular batteries. In contrast to batteries, which are prone to fail when short-circuited, supercapacitors don’t heat up as well because they have a lower internal resistance.
Due to their extremely charged condition, shorting a supercapacitor may induce electrical arcing and likely damage the system, but unlike a battery, the produced heat is not a problem.
Applications
Supercapacitors are better used for applications where a fast charge is required to fuel a short-term need, while batteries are selected for longer-term energy supply. Using a hybrid battery achieves all of these objectives when reducing battery stress, resulting in longer battery life.
Can Supercapacitors Replace Batteries?
The answer relies heavily on the application. Some advantages and some drawbacks are associated with both of them. Batteries are nearly two-and-a-half times as thick as supercapacitors. It means that they are ideal for higher energy density systems or machines with short battery lifespans. Batteries are less efficient than supercapacitors. They’re the ideal type of battery for charging an electric car.
Summing Up Future uses of supercapacitors would be mobile phones, tablets, hybrid vehicles, and other gadgets operating on batteries. From a realistic standpoint, the most thrilling benefit is their extremely rapid charging time, which ensures that plugging the electric car into a charger for some minutes will charge the battery.




Leave a Reply